Wonder what is quantum physics? What a dummy you are! Get these 10 amazing quantum physics facts with pictures for dummies. Your world will never be the same after you take a look at these discoveries:
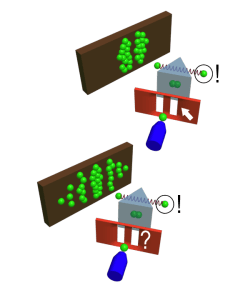
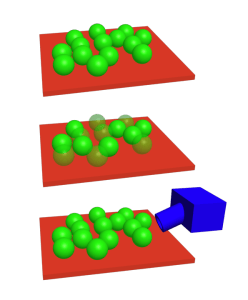
1. Wave function collapse
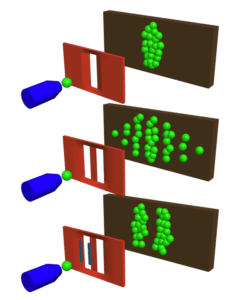
In 1803, Thomas Young sent a beam of light through an opaque plate with two slits in it. Instead of seeing the expected two lines on the viewing screen, he saw several lines, as if two waves of light from the two slits had been interfering (overlapping) with each other. It was the beginning of quantum physics. Every dummy should know it! Over the 20th and 21st centuries, it has been proven that not only light, but also individual elementary particles and even some molecules behave as waves – as if they were going through both slits at the same time. However, if you place a sensor at the slits that observes what exactly happens to the particle at that point, and which slit it finally ends up going through, then only two lines will appear on the projection screen, as if the fact of observation (indirect influence) collapses the wave function and the experiment subject behaves as a particle.